Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Infection
- Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Iranian children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Farhad Sarrafzadeh, Seyed Mojtaba Sohrevardi, Hamid Abousaidi, Hossein Mirzaei
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(8):415-421. Published online November 20, 2020
-

The pooled prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) was 42% among culture-positive cases of S. aureus, 51% in hospitalized children, and 14% in healthy children. The high prevalence of MRSA in Iranian children may be due to insufficient infection control measures in hospitals, inappropriate use of methicillin, inadequate staff training, and over-prescription of antibiotics in Iran.
- Review Article
- Infection
- The COVID-19 pandemic: an unprecedented tragedy in the battle against childhood obesity
- Maximilian Andreas Storz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):477-482. Published online November 5, 2020
-

Large-scale quarantine and home confinement during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic will impose new and unfamiliar stressors on children, thereby worsening the childhood obesity epidemic. Physical, nutritional, and psychosocial factors that promote obesity in children during this special situation complementarily contribute to an unprecedented obesogenic environment. Involved stakeholders, including governments, schools, and families, must make all efforts to minimize the impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on childhood obesity.
- Original Article - Clinical trial
- WITHDRAWN:Randomized controlled trial of effect of N-acetylcysteine as an antioxidant on iron overload in children with thalassemia major
- Yasmen A Mohamed, Mohamed H Meabed, Amany Ashraf, Dalia S Morgan, Mostafa G Abdul Latif, Rehab M Abd-Elkareem, Heba M Ahmed
-
Background: β-Thalassemias are characterized by the presence of mutations in the globin gene that result in the absence or reduced synthesis of β-globin chains of the hemoglobin tetramer. Several studies have reported increased oxidative stress in β-thalassemia major (β-TM) patients. N-acetylcysteine (NAC), a derivative of L-cysteine amino acid, is commonly used as a mucolytic drug. Numerous studies have reported efficient... -
- Original Article
- Allergy
- Influence of age at complementary food introduction on the development of asthma and atopic dermatitis in Korean children aged 1–3 years
- Jihyun Lee, Meeyong Shin, Bora Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(8):408-414. Published online November 1, 2020
-

Question: Is age at the time of complementary food introduction associated with asthma and atopic dermatitis (AD) in early childhood?
Finding: We found no significant association between age at the time of complementary food introduction and the incidence of AD and asthma in Koreans aged 1–3 years.
Meaning: Our findings suggest that the influence of individual allergenic foods on the development of AD and asthma should be clarified.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Expression profiling of cultured podocytes exposed to nephrotic plasma reveals intrinsic molecular signatures of nephrotic syndrome
- Stuti Panigrahi, Varsha Chhotusing Pardeshi, Karthikeyan Chandrasekaran, Karthik Neelakandan, Hari PS, Anil Vasudevan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(7):355-363. Published online November 1, 2020
-
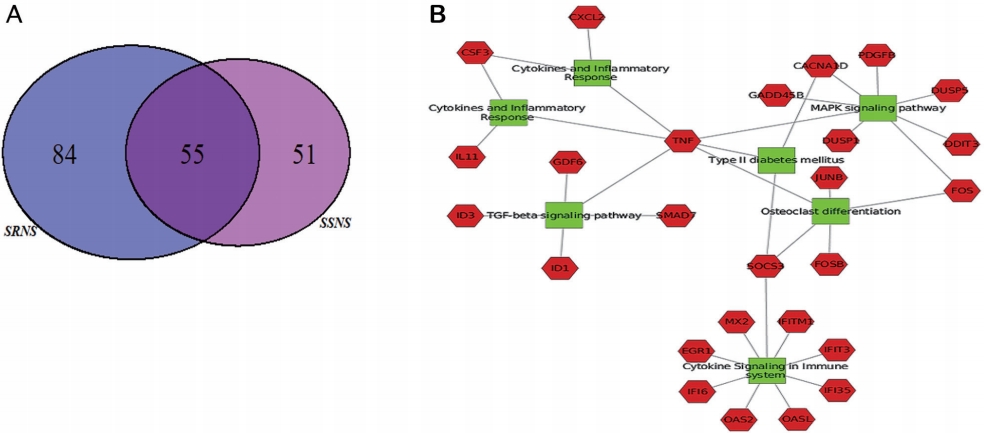
Question: Is it possible to classify nephrotic syndrome (NS) through gene expression profiling of podocytes exposed to NS plasma?
Finding: Our data showed different expression profiles in podocytes exposed to nephrotic plasma from different clinical groups, suggesting the molecular stratification of patients into intrinsic subtypes.
Meaning: Transcriptome profiling of podocytes treated with NS plasma can stratify patients into intrinsic subtypes and provide insight into the molecular mechanisms of podocyte injury.
- Gastroenterology
- Celiac disease in children: Increasing prevalence and changing clinical presentations
- Hasan M. Isa, Eman Farid, Jaafar J. Makhlooq, Afaf M. Mohamed, Jumana G. Al-Arayedh, Fawzeya A. Alahmed, Shima Medani
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(6):301-309. Published online October 17, 2020
-
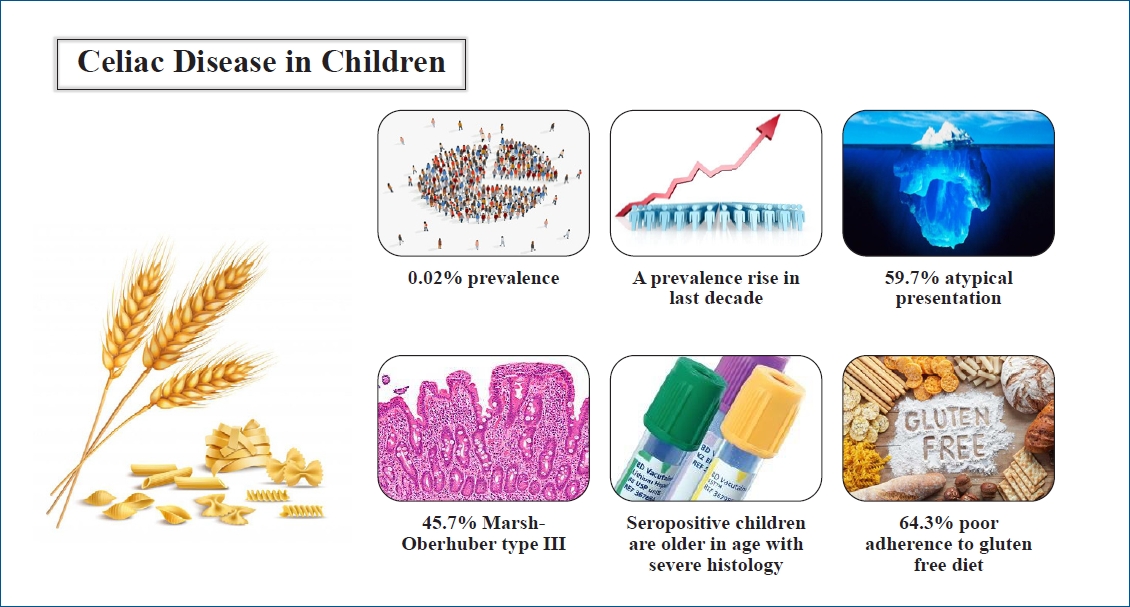
Question: What are the prevalence and clinical characteristics of celiac disease (CD) in children in Bahrain?
Finding: We found a significant increase in CD prevalence over the last decade (P=0.0001). A male predominance was noted. Atypical presentations were common. Most patients had poor adherence to a gluten-free diet.
Meaning: CD is an underdiagnosed condition. Atypical symptoms should be considered to prevent missing patients with CD.
- Endocrinology
- Zinc transporter 8 autoantibody in the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes in children
- Nur Rochmah, Muhammad Faizi, Siti Wahyu Windarti
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):402-405. Published online October 6, 2020
-
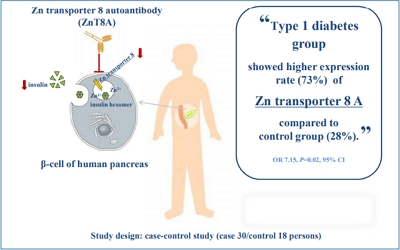
Question: Can zinc transporter 8 autoantibody (ZnT8A) be used for diagnosing type 1 diabetes (T1D)?
Finding: Twenty-two of 30 subjects with type 1 diabetes (73.3 %) were positive for ZnT8A compared to 5 of 18 controls (27.8%).
Meaning: ZnT8A has potential for clinical applications in the diagnosis of T1D.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Causes of acute gastroenteritis in Korean children between 2004 and 2019
- Eell Ryoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(6):260-268. Published online September 18, 2020
-
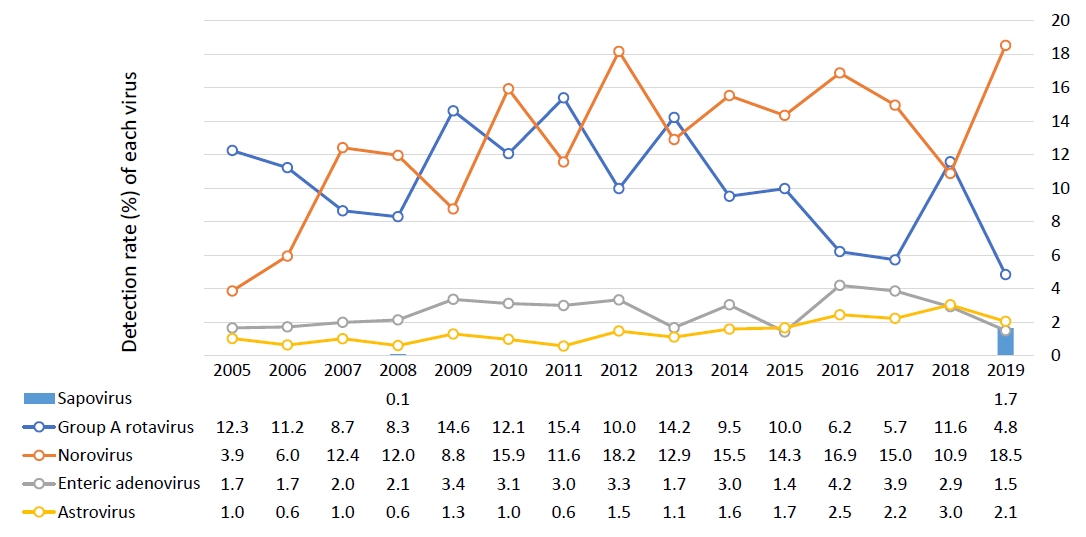
· Norovirus is the most common virus in Korean children with acute gastroenteritis.
· Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. are the most common cause of bacterial gastroenteritis in Korean children, with a detection rate of 3%–20%.
· Uncommon bacterial and parasitic gastroenteritis require attention because of increasing international exchange and overseas travel.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Value of the International Classification of Diseases code for identifying children with biliary atresia
- Pornthep Tanpowpong, Chatmanee Lertudomphonwanit, Pornpimon Phuapradit, Suporn Treepongkaruna
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(2):80-85. Published online August 24, 2020
-
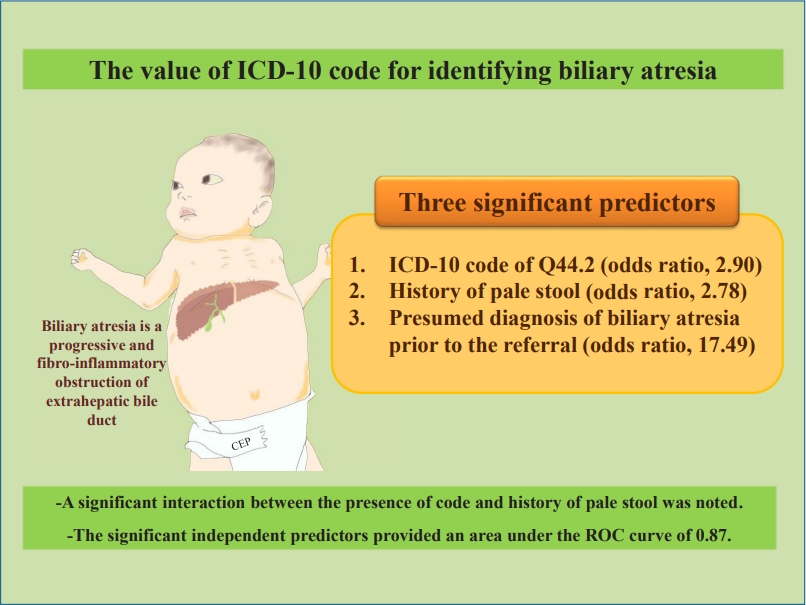
Question: What is the value of the diagnostic code in identifying cases of biliary atresia in a large administrative database?
Finding: The diagnostic code’s accuracy and sensitivity are acceptable for identifying algorithm-defined cases. A history of pale stool and a presumed diagnosis of biliary atresia prior to referral added value.
Meaning: The addition of clinical data to the diagnostic code significantly increased the diagnostic yield.
- Review Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- The use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in children with acute fulminant myocarditis
- Silver Heinsar, Sainath Raman, Jacky Y. Suen, Hwa Jin Cho, John F. Fraser
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(5):188-195. Published online August 10, 2020
-
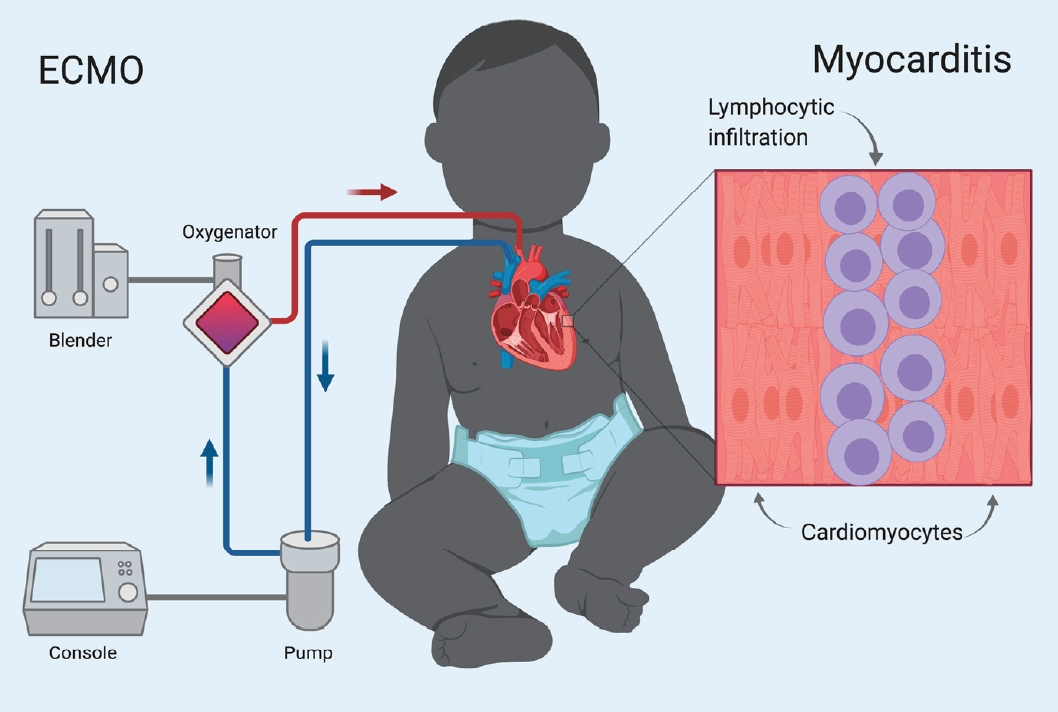
Acute fulminant myocarditis (AFM) occurs as an inflammatory response to an initial myocardial insult. Its rapid and deadly progression calls for prompt diagnosis with aggressive treatment measures. The demonstration of its excellent recovery potential has led to increasing use of mechanical circulatory support, especially extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). Arrhythmias, organ failure, elevated cardiac biomarkers, and decreased ventricular function at presentation...
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Evaluating the effects of probiotics in pediatrics with recurrent abdominal pain
- Parisa Rahmani, Azin Ghouran-orimi, Farzaneh Motamed, Alireza Moradzadeh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):485-490. Published online July 21, 2020
-
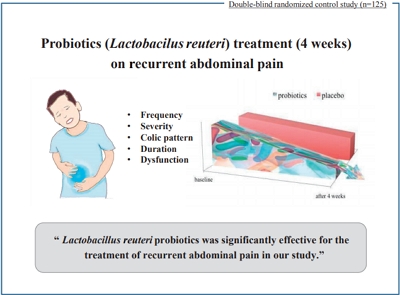
Question: ecurrent abdominal pain (RAP) is a chief complaint among pediatrics and is associated with reduced quality of life, for both parent and child, and economic burden. Does probiotics reduce the frequency of RAP among children?
Finding: This study reported the effects of Lactobacillus reuteri probiotics among children with RAP as a result of multiple etiologies.
Meaning: The administration of probiotic supplements is significantly associated with pain relief among RAP children presented with functional abdominal pain, irritable bowel syndrome, and functional dyspepsia.
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- Overview of management of children with COVID-19
- Dyah Kanya Wati, Arya Krisna Manggala
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):345-354. Published online July 17, 2020
-
The specific treatments for COVID-19 in children remain inconclusive and debatable despite effectively decreasing its signs and symptoms.
The need for clinical trials and reports should be investigated.
- Gastroenterology
- Changing prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in children and adolescents
- Ji Sook Park, Jin Su Jun, Ji-Hyun Seo, Hee-Shang Youn, Kwang-Ho Rhee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):21-25. Published online July 15, 2020
-
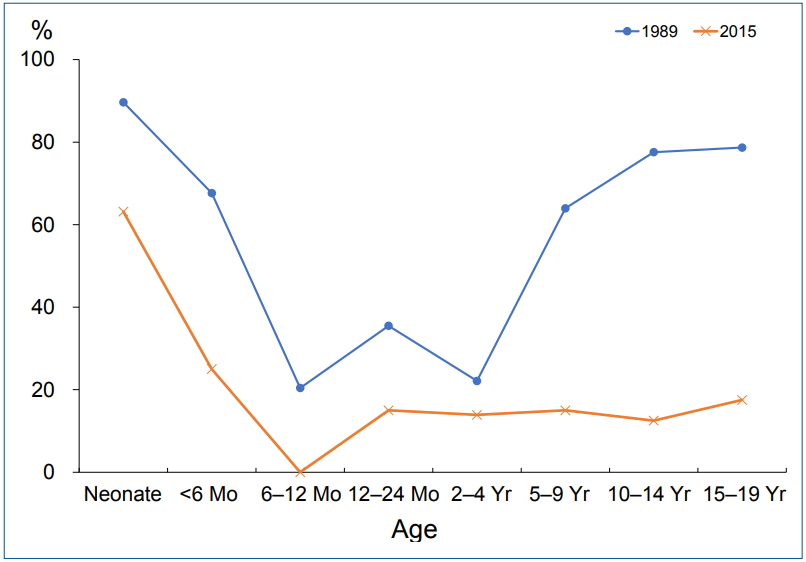
Although Helicobacter pylori infection rate in children is unclear due to diversity and limitation of diagnostic tests unlike in adults, investigation the childhood prevalence is important for predicting H. pylori-related diseases in the future.
H. pylori infection occurred in early childhood, and declined during 30 years in our study.
Change in risk factors of H. pylori transmission and consensus for eradication therapy in children might further reduce the infection rate.
- Original Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Sonographic renal length and volume of normal Thai children versus their Chinese and Western counterparts
- Chantima Rongviriyapanich, Thanarat Sakunchit, Chirawat Sudla, Supamas Mungkung, Napapong Pongnapang, Chai Hong Yeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):491-498. Published online July 13, 2020
-
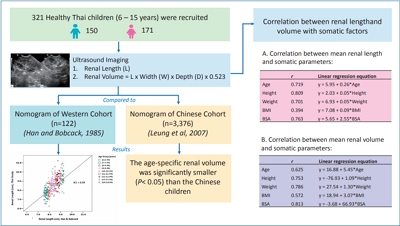
Question: What is the normal renal size of Thai children and is the renal nomogram comparable to those of Western and Chinese cohorts?
Finding: The renal length of Thai children was moderately correlated with that of Western children, while the age-specific renal volume was significantly smaller than that of Chinese children.
Meaning: Renal size in children can vary among regions and sociodemographic backgrounds; hence, a local reference standard is needed.
- Review Article
- Other
- Review of epidemiological studies on air pollution and health effects in children
- Jong-Tae Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):3-11. Published online June 10, 2020
-
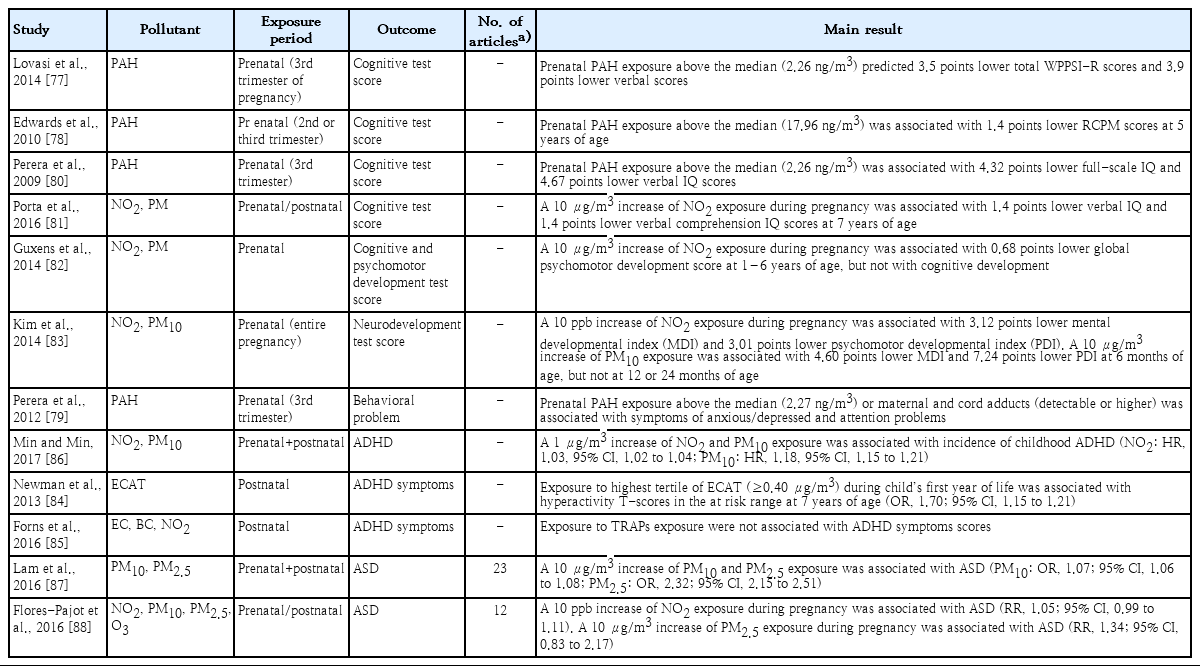
This review summarized the accumulated epidemiologic evidence with emphasis on studies conducted in Korea and heterogeneity in the literature. Based on systematic reviews and meta-analyses, there is consistent evidence on the association between exposure to ambient air pollution and children’s health, especially respiratory health and adverse birth outcomes, and growing evidence on neurodevelopmental outcomes.
- Pulmonology
- Current perspectives on atypical pneumonia in children
- Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):469-476. Published online June 10, 2020
-
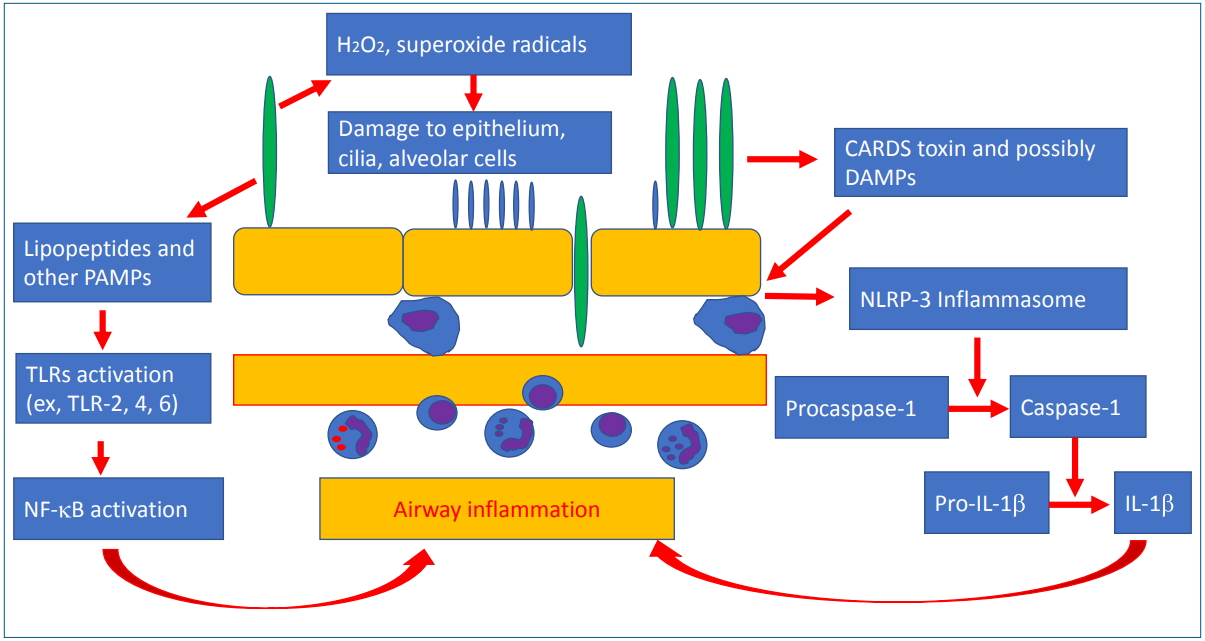
Macrolides are the first line treatment in atypical pneumonia caused by M. pneumoniae, C. pneumoniae, and L. pneumophila. Macrolide-resistant mycoplasma pneumonia (MRMP) is emerging worldwide, especially in East Asia. Immune modulators such as corticosteroids or second line antibiotics are treatment options for MRMP. Pediatricians should be careful with empirical therapy of macrolides in children with mild to moderate community-acquired pneumonia not to increase the risk of MRMP.
- Neurology
- Health effects of electromagnetic fields on children
- Jin-Hwa Moon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(11):422-428. Published online May 26, 2020
-
· The nervous systems of children are more vulnerable to the effects of electromagnetic waves than adults.
· The exposure to electromagnetic fields (EMFs) among children should be minimized.
· According to International Agency for Research on Cancer EMFs are possibly carcinogenic, it should not be overlooked or interpreted with bias.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Efficacy of conservative treatment of perianal abscesses in children and predictors for therapeutic failure
- Lars Boenicke, Johannes Doerner, Stefan Wirth, Hubert Zirngibl, Mike Ralf Langenbach
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):272-277. Published online May 15, 2020
-
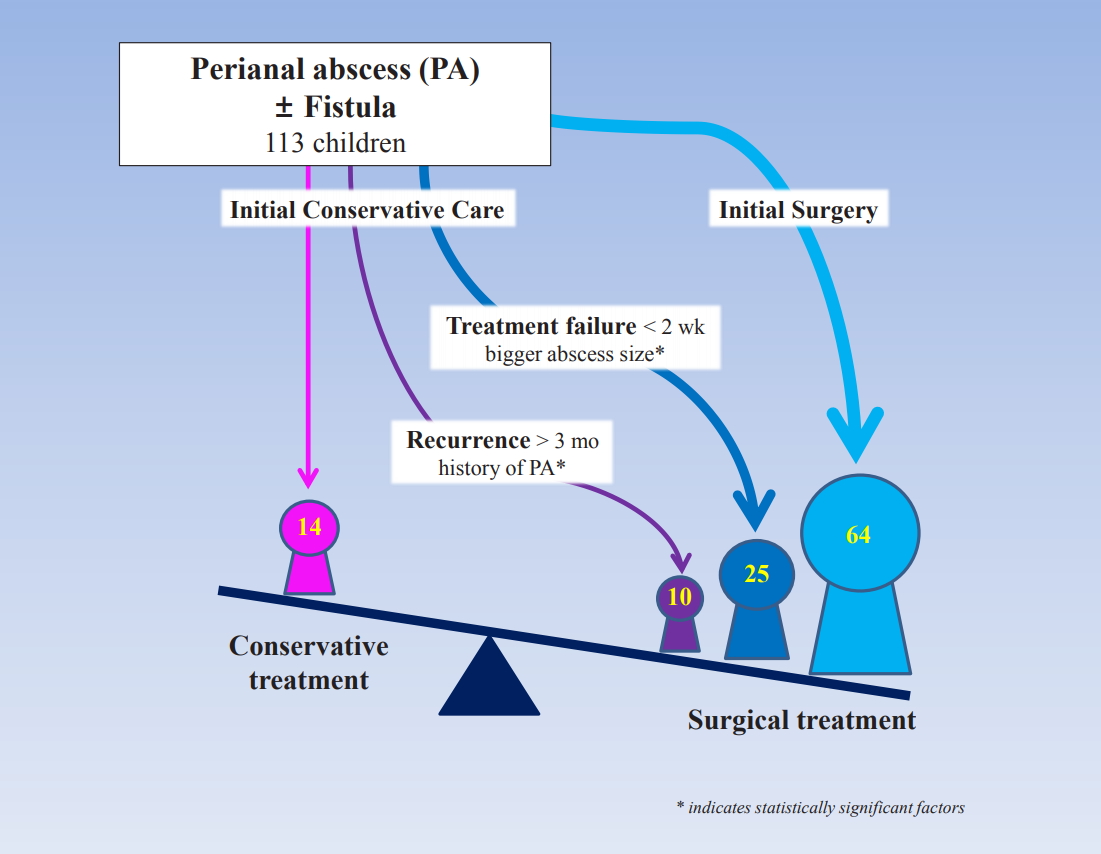
Background: The optimal management of perianal abscess in children is controversial.
Purpose: To evaluate the efficiency of conservative treatment of perianal abscess in children and identify parameters that predict therapy failure. Methods: All cases of children younger than 14 years of age with perianal abscesses between 2001–2016 were evaluated. Results: Of the 113 enrolled patients, 64 underwent subsequent surgery for advanced disease (primary...
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Pollen-food allergy syndrome in children
- You Hoon Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):463-468. Published online May 14, 2020
-

The prevalence of pollen-food allergy syndrome (PFAS) in Korean children with pollen allergy was recently reported to be 42.7%. PFAS can cause a wide range of symptoms from mild allergy to severe anaphylaxis depending on the nature of food allergens that share the epitopes with pollen. Cases of anaphylaxis caused by PFAS have recently increased. Treatments for PFAS should be individualized for patients according to the severity of symptoms.
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Development of the Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST)
- Hee Jung Chung, Donghwa Yang, Gun-Ha Kim, Sung Koo Kim, Seoung Woo Kim, Young Key Kim, Young Ah Kim, Joon Sik Kim, Jin Kyung Kim, Cheongtag Kim, In-Kyung Sung, Son Moon Shin, Kyung Ja Oh, Hee-Jeong Yoo, Hee Joon Yu, Seoung-Joon Lim, Jeehun Lee, Hae-Ik Jeong, Jieun Choi, Jeong-Yi Kwon, Baik-Lin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(11):438-446. Published online May 14, 2020
-
Question: Can the Korean Developmental Screening Test for Infants and Children (K-DST) be a useful screening tool for infants and children in Korea?
Finding: The K-DST has high reliability (internal consistency of 0.73–0.93, test-retest reliability of 0.77–0.88) and a high discriminatory ability with a sensitivity of 0.833 and specificity of 0.979.
Meaning: The K-DST is an effective and reliable screening tool for infants and children with neurodevelopmental disorders in Korea.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Epidemiology and clinical features of coronavirus disease 2019 in children
- Soo-Han Choi, Han Wool Kim, Ji-Man Kang, Dong Hyun Kim, Eun Young Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(4):125-132. Published online April 6, 2020
-
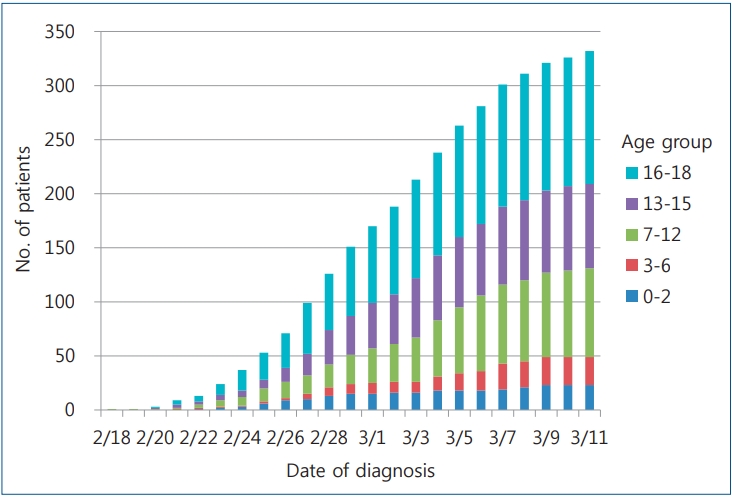
Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), which started in Wuhan, China, in December 2019 and declared a worldwide pandemic on March 11, 2020, is a novel infectious disease that causes respiratory illness and death. Pediatric COVID-19 accounts for a small percentage of patients and is often milder than that in adults; however, it can progress to severe disease in some cases. Even neonates...
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Influence of subclinical hypothyroidism on metabolic parameters in obese children and adolescents
- Ozlem Kara
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(3):110-114. Published online March 6, 2020
-

Question: Does subclinical hypothyroidism in obese children and adolescents affect metabolic parameters?
Finding: Insulin, HOMA-IR, and TG levels were higher and the HDL-C level was lower in patients with SH.
Meaning: A clear association is observed between SH, and insulin resistance and dyslipidemia in obese children. It can be said that the TSH may be evaluated as a metabolic risk factor in obese patients.
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Advanced neuroimaging techniques for evaluating pediatric epilepsy
- Yun Jeong Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(3):88-95. Published online February 6, 2020
-
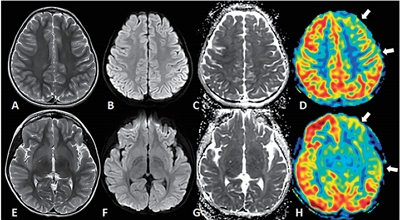
Accurate localization of the seizure onset zone is important for better seizure outcomes and preventing deficits following epilepsy surgery. Recent advances in neuroimaging techniques have increased our understanding of the underlying etiology and improved our ability to noninvasively identify the seizure onset zone. Using epilepsy-specific magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) protocols, structural MRI allows better detection of the seizure onset zone,...
- Allergy
- Montelukast use over the past 20 years: monitoring of its effects and safety issues
- Yong Ju Lee, Chang-Keun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):376-381. Published online February 5, 2020
-
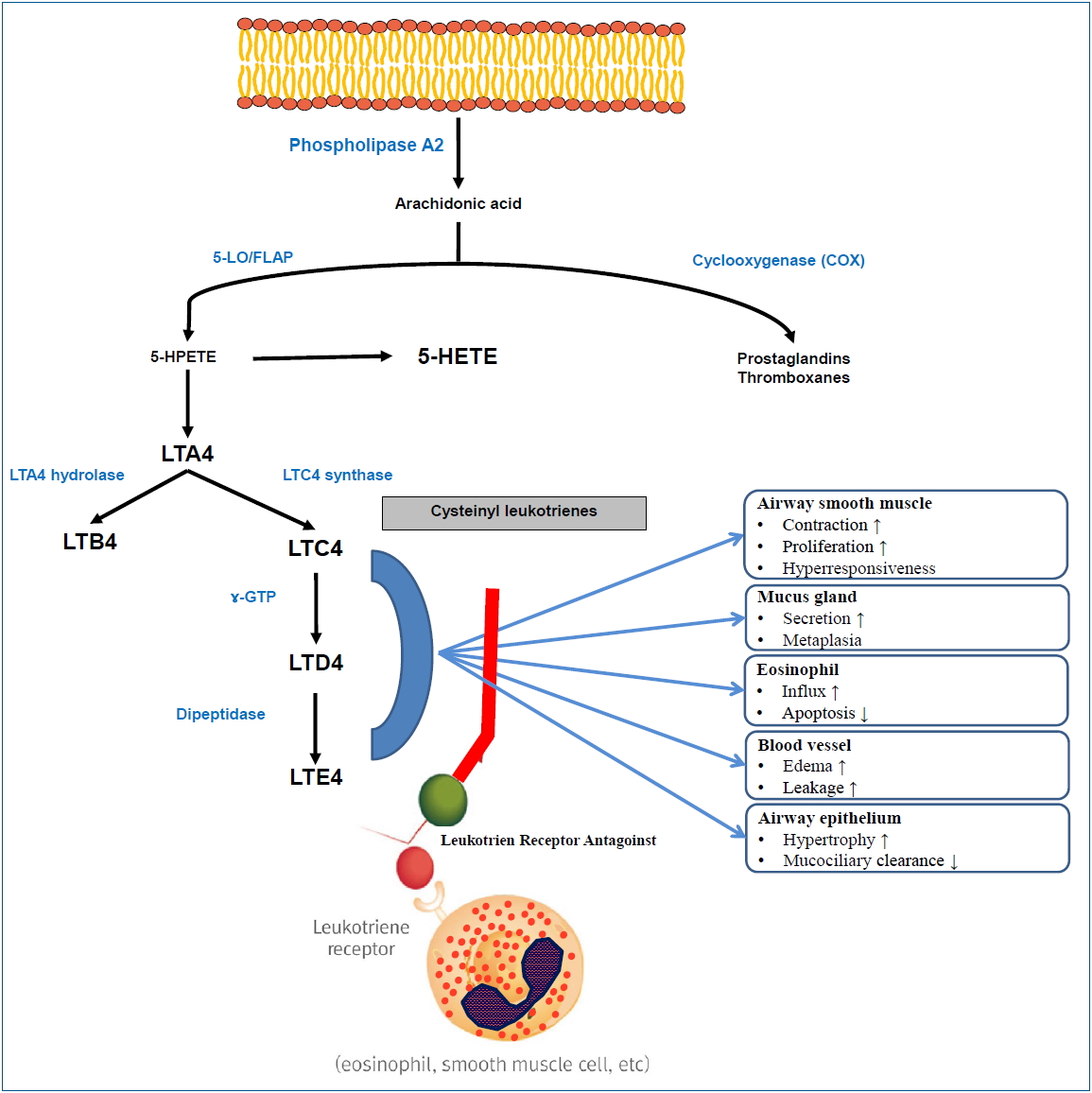
Although the efficacy of montelukast is inferior to that of ICS, both physicians and parents prefer montelukast to ICSs.
EDN may be a useful biomarker for the treatment and monitoring of preschool children with asthma.
The US FDA requires boxed warning about serious neuropsychiatric events of montelukast, therefore, physicians should consider the benefits and risks of montelukast before prescribing it.
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Ability of children to perform touchscreen gestures and follow prompting techniques when using mobile apps
- Savita Yadav, Pinaki Chakraborty, Arshia Kaul, Pooja, Bhavya Gupta, Anchal Garg
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(6):232-236. Published online February 5, 2020
-

Background: Children today get access to smartphones at an early age. However, their ability to use mobile apps has not yet been studied in detail.
Purpose: This study aimed to assess the ability of children aged 2–8 years to perform touchscreen gestures and follow prompting techniques, i.e., ways apps provide instructions on how to use them. Methods: We developed one mobile app...
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Variation in clinical usefulness of biomarkers of acute kidney injury in young children undergoing cardiac surgery
- Hee Sun Baek, Youngok Lee, Hea Min Jang, Joonyong Cho, Myung Chul Hyun, Yeo Hyang Kim, Su-Kyeong Hwang, Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(4):151-156. Published online February 5, 2020
-
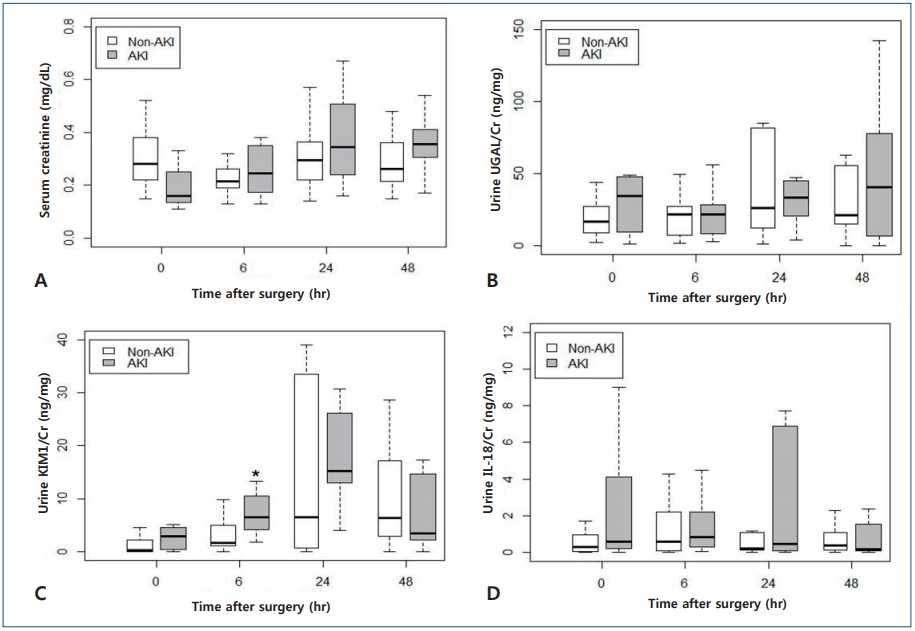
Question: Can clinical usefulness of biomarkers of acute kidney injury vary on the clinical circumstances?
Finding: In young children undergoing cardiac surgery, urine KIM-1/Cr level peaked at 24 hours with significant difference from baseline level and was significantly higher at 6 hours in the AKI group. However, urine NGAL/Cr and IL-18/Cr levels showed no specific trend with time for 48 hours after cardiac surgery.
Meaning: Urine KIM-1/Cr concentration could be considered a good biomarker for early AKI prediction after open cardiac surgery in young children.
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- The past, present, and future of humidifier disinfectant-associated interstitial lung diseases in children
- Eun Lee, So-Yeon Lee, Soo-Jong Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):251-258. Published online December 9, 2019
-
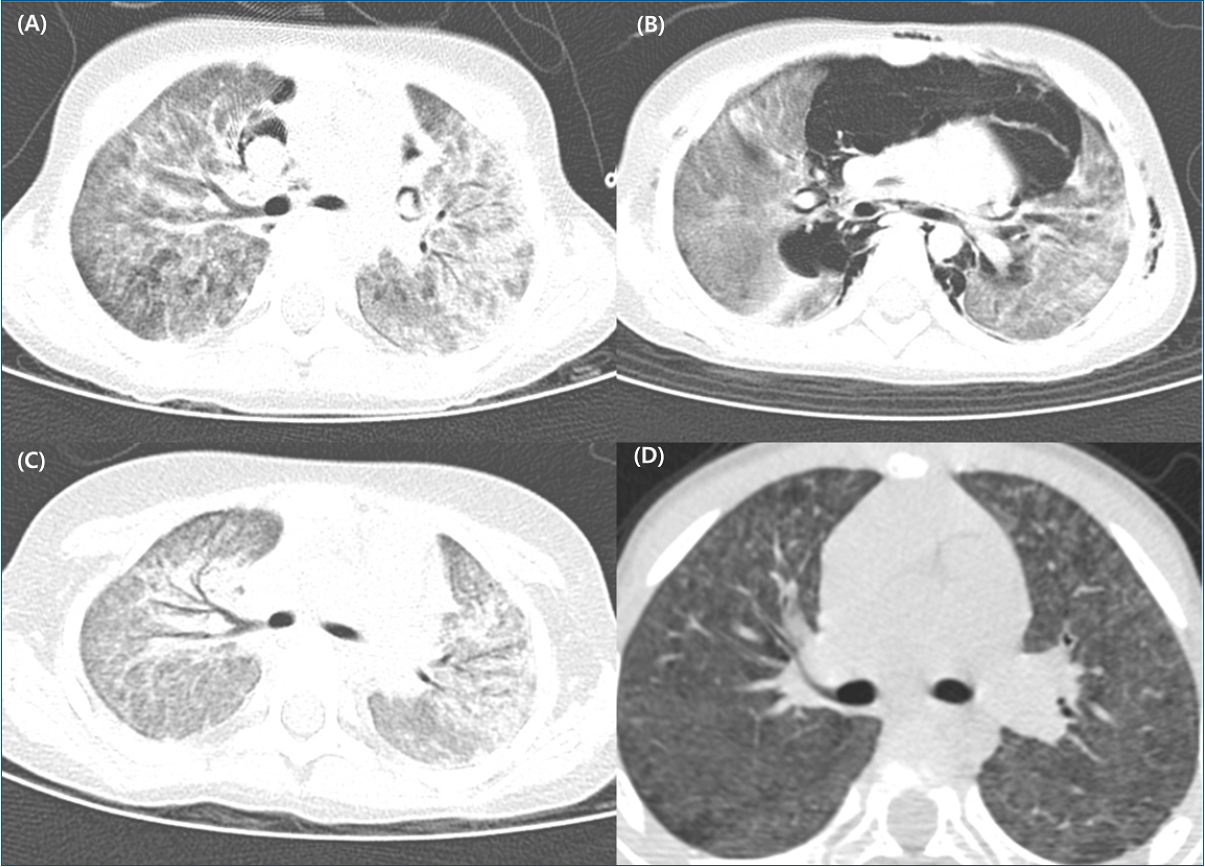
Exposure to environmental factors can cause interstitial lung diseases (ILDs); however, such types of ILDs are rare. From 2007 to 2011, an ILD epidemic occurred in South Korea owing to inhalational exposure to toxic chemicals in humidifier disinfectants (HDs). HD-associated ILDs (HD-ILDs) are characterized by rapidly progressing respiratory failure with pulmonary fibrosis and a high mortality rate of 43.8%−58.0%. Although...
- Original Article
- Other
- Korean parents’ perceptions of the challenges and needs on school re-entry during or after childhood and adolescent cancer: a multi-institutional survey by Korean Society of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology
- Jun Ah Lee, Jae Min Lee, Hyeon Jin Park, Meerim Park, Byung Kiu Park, Hee Young Ju, Ji Yoon Kim, Sang Kyu Park, Young Ho Lee, Ye Jee Shim, Heung Sik Kim, Kyung Duk Park, Yeon-Jung Lim, Hee Won Chueh, Ji Kyoung Park, Soon Ki Kim, Hyoung Soo Choi, Hyo Seop Ahn, Jeong Ok Hah, Hyoung Jin Kang, Hee Young Shin, Mee Jeong Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(4):141-145. Published online November 14, 2019
-
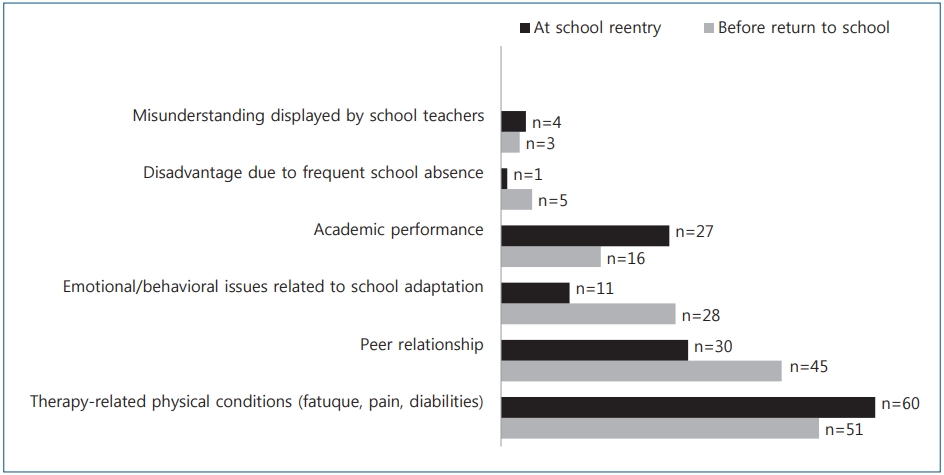
Question: What are the parental needs and challenges when their children return to school after cancer?
Finding: In addition to scholastic aptitude-oriented programs, emotional and psychosocial support is necessary for a successful return to school.
Meaning: Pediatric oncologists should actively engage in improving oncology practices to better integrate individualized school plans and educate peers and teachers to improve health literacy to make them understand the needs of children with cancer.
- Allergy
- Asthma predictive index as a useful diagnostic tool in preschool children: a cross-sectional study in Korea
- Dong Hyeon Lee, Ji-Won Kwon, Hyung Young Kim, Ju-Hee Seo, Hyo-Bin Kim, So-Yeon Lee, Gwang-Cheon Jang, Dae-Jin Song, Woo Kyung Kim, Young-Ho Jung, Soo-Jong Hong, Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(3):104-109. Published online November 8, 2019
-

Question: Is physician-diagnosed current asthma in preschool children associated with the asthma predictive index, atopic sensitization, or pulmonary function test?
Finding: Physician-diagnosed current asthma in preschool children was associated with the asthma predictive index, but not with spirometry, methacholine provocation test, fractional expiratory nitric oxide level, and atopic sensitization.
Meaning: Physician-diagnosed asthma in preschool children may be different from classic atopic asthma in school children or adolescents.
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy in children: a clinical review
- Ji-Won Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(1):3-7. Published online October 28, 2019
-
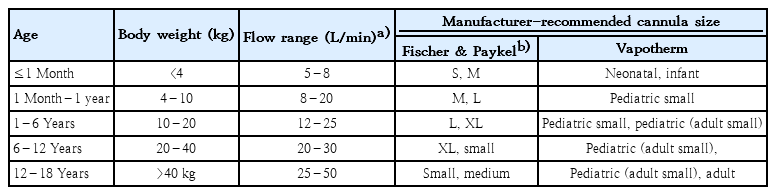
High-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) is a relatively safe and effective noninvasive ventilation method that was recently accepted as a treatment option for acute respiratory support before endotracheal intubation or invasive ventilation. The action mechanism of HFNC includes a decrease in nasopharyngeal resistance, washout of dead space, reduction in inflow of ambient air, and an increase in airway pressure. In preterm...
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







